The State of the U.S. Economy (May 2023)
- IFWF

- May 14, 2023
- 3 min read
Mr. Fan Yang, Economics Ph.D. candidate
© International Foundation for World Freedom
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is one of the most commonly used measures of a country's economic activity. It represents the total value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders over a given period of time. A high GDP indicates a strong economy, while a low GDP suggests a weaker economy.
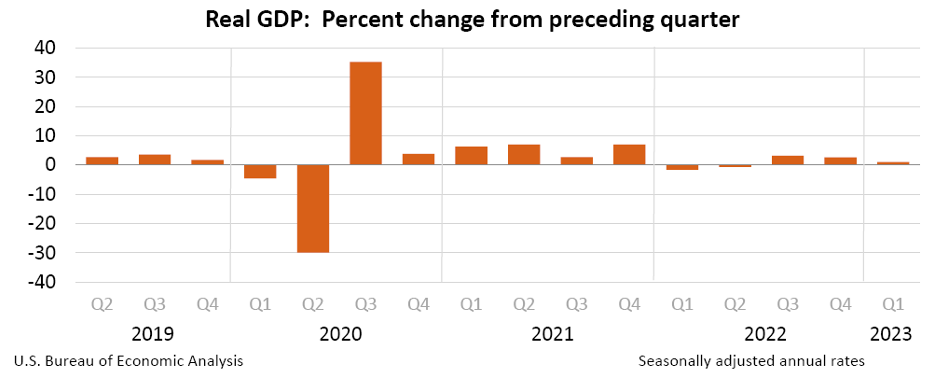
In the first quarter of 2023, the U.S. economy continued to grow, but at a slower pace than in the previous quarter. Real GDP increased at an annual rate of 1.1 percent, down from the 2.6 percent rate in the last quarter of 2022. Nonetheless this was the third consecutive quarter of growth after output declined in the first half of 2022.
Compared to the previous quarter, the slowdown in real GDP growth during the first quarter of 2023 was primarily due to a downturn in private inventory investment and a slowdown in nonresidential fixed investment. However, this was partially offset by an acceleration in consumer spending, an upturn in exports, and a smaller decrease in residential fixed investment. Additionally, imports turned up.
Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate is an important economic indicator that measures the percentage of the labor force that is currently unemployed but actively seeking employment. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) releases monthly reports on the national unemployment rate and state-level unemployment rates.
According to the BLS, the national unemployment rate was 3.4 percent in January 2023, which increased slightly to 3.6 percent in February 2023. However, in March 2023, the unemployment rate edged down to 3.5 percent. Meanwhile, the labor force participation rate edged up to 62.6 percent in March from 62.5 percent in February, the highest since March 2020.
In March 2023, the unemployment rates were lower in 18 states, higher in the District of Columbia, and stable in 32 states. The state with the lowest unemployment rate was South Dakota, at 1.9 percent, while the highest rate was in the Nevada, at 5.5 percent.

Inflation Rate
Inflation is a key indicator of the overall health of an economy, and it is defined as the rise in prices of goods and services in an economy. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure of the change in prices of goods and services paid by consumers. It is often used as a gauge for inflation.
In July 2022, the inflation rate in the U.S., as measured by the CPI, was 8.5%. However, as of March 2023, the annual inflation rate has decreased for the ninth consecutive period to 5%, which is the lowest since May 2021, down from 6% in February. The lower inflation rate was mainly due to a slower increase in food prices and a fall in energy costs. However, inflation for shelter, which accounts for over 30% of the total CPI basket, continued to rise.
Overall, the US inflation rate in the first quarter of 2023 remained elevated but showed some signs of moderation, driven by a mixed picture of price movements across different categories. The trend and direction of inflation will continue to be an important factor in shaping the economic outlook and policy decisions

Interest Rate
Interest rates play a crucial role in the functioning of the U.S. economy, impacting borrowing, spending, and investment decisions. In basic terms, interest rates are the cost of borrowing money, and they can be set by the Federal Reserve to achieve specific economic goals.
The Federal Reserve, commonly referred to as the "Fed," is responsible for setting monetary policy in the U.S. The primary goal of the Fed is to maintain low inflation and unemployment rates, and it does this by controlling interest rates.
During the first quarter of 2023, the Fed implemented its ninth interest rate hike since March 2022, increasing the benchmark federal funds rate to a target range between 4.75%-5%. This rate sets the cost of borrowing between banks for overnight lending, but it also has a ripple effect on consumer debt, such as mortgages, auto loans, and credit cards.
The Fed's interest rate decisions can impact the economy in various ways. Higher interest rates can discourage borrowing and spending, which can slow down economic growth but can also help curb inflation. Lower interest rates, on the other hand, can encourage borrowing and spending, which can stimulate economic growth but also increase the risk of inflation.






Comments